Itolizumab compared to standard of care for moderate to severe COVID-19
Explanations
a. Downgraded by two levels for serious imprecision due to very small sample size contributed by single study with low event rates , and further one level for the high risk of bias as it is a single trial with high risk of bias in one domain and some concerns for two other domains in RoB 2 tool.
b. Downgraded by two levels for serious imprecision due to very small sample size contributed by single study with wide 95% Confidence interval
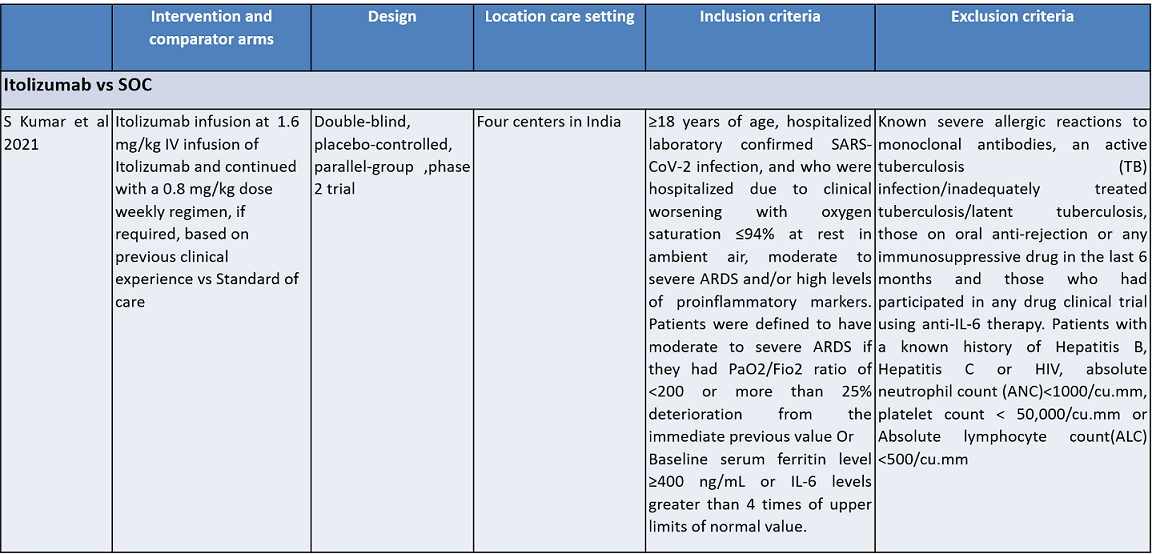
Itolizumab is an anti-CD6 humanized monoclonal antibody; it works by suppressing T-cell activation and downregulates the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules. It was initially developed for various cancers. It was approved in India to treat moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis in 2013. Itolizumab is now being re-purposed for COVID-19. The potential utility of Itolizumab in COVID-19 was proposed first in Cuba with the approval of a single-arm clinical trial. It expanded access use is based on its unique mechanism of action in alleviating cytokine release syndrome. Subsequently, after receiving regulatory permission, a phase II, open-label, randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted in 30 COVID-19 patients in India. Based on its results, the Indian drug regulatory agency recently approved Itolizumab in July 2020 for 'restricted emergency use' to treat CRS in moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) due to COVID-191.
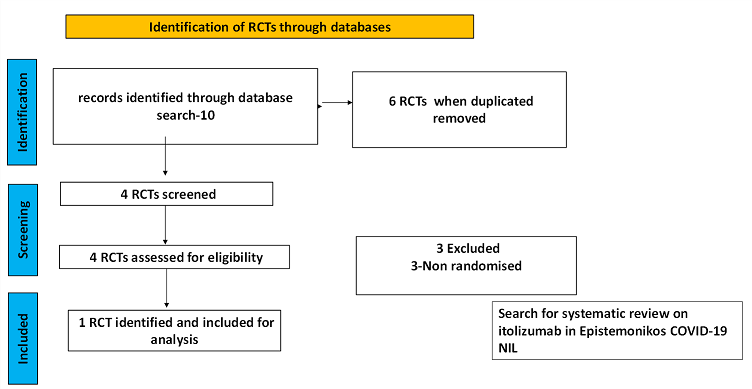
To identify all available systematic reviews pertaining to our PICO question, a systematic search of PubMed, covid-nma.org and the Epistemonikos databases was conducted. The search strategy was designed and validated by the Group’s information specialist. The search results were screened independently by two reviewers against the pre-defined criteria set out above, using Rayyan.
There was no systematic review available in the databases referred to. For randomized controlled trials, 6 were identified using databases, of which 2 were removed as they were duplicates. Of the 4 RCTs screened, 3 were non-randomised controlled trials and hence they were excluded. The remaining 1 RCT was assessed for eligibility and included for analysis.
For the risk of bias, Cochrane ROB2 tool was used. For all outcomes, one review author performed the assessment, and cross-checked it against the assessment by another review author. If there was a difference in more than one domain, it was assessed by a third independent author.
Data was entered into Review manager version 5.4 for meta-analysis. The results were entered into Grade ProGDT (online), to create the summary of findings (GRADE) table. We used risk ratios (RR) for dichotomous outcomes with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Population – Inpatients with moderate to severe Covid-19 infection
Intervention – Itolizumab
Control – standard of care
Following were the outcomes we wanted to extract data for:
Primary:
1. Overall mortality
2. Time to clinical recovery
Secondary:
1. Length of hospital stay
2. Need for NIV/invasive mechanical ventilation
3. Duration of invasive ventilation
4. Duration of stay in ICU care
Adverse events:
a) All
b) Serious
c) Infusion-related adverse events
We found 1 randomized controlled trial that met our search criteria. However, this was a single trial with very low sample size of 30 and a high risk of bias as assessed by RoB 2 tool.
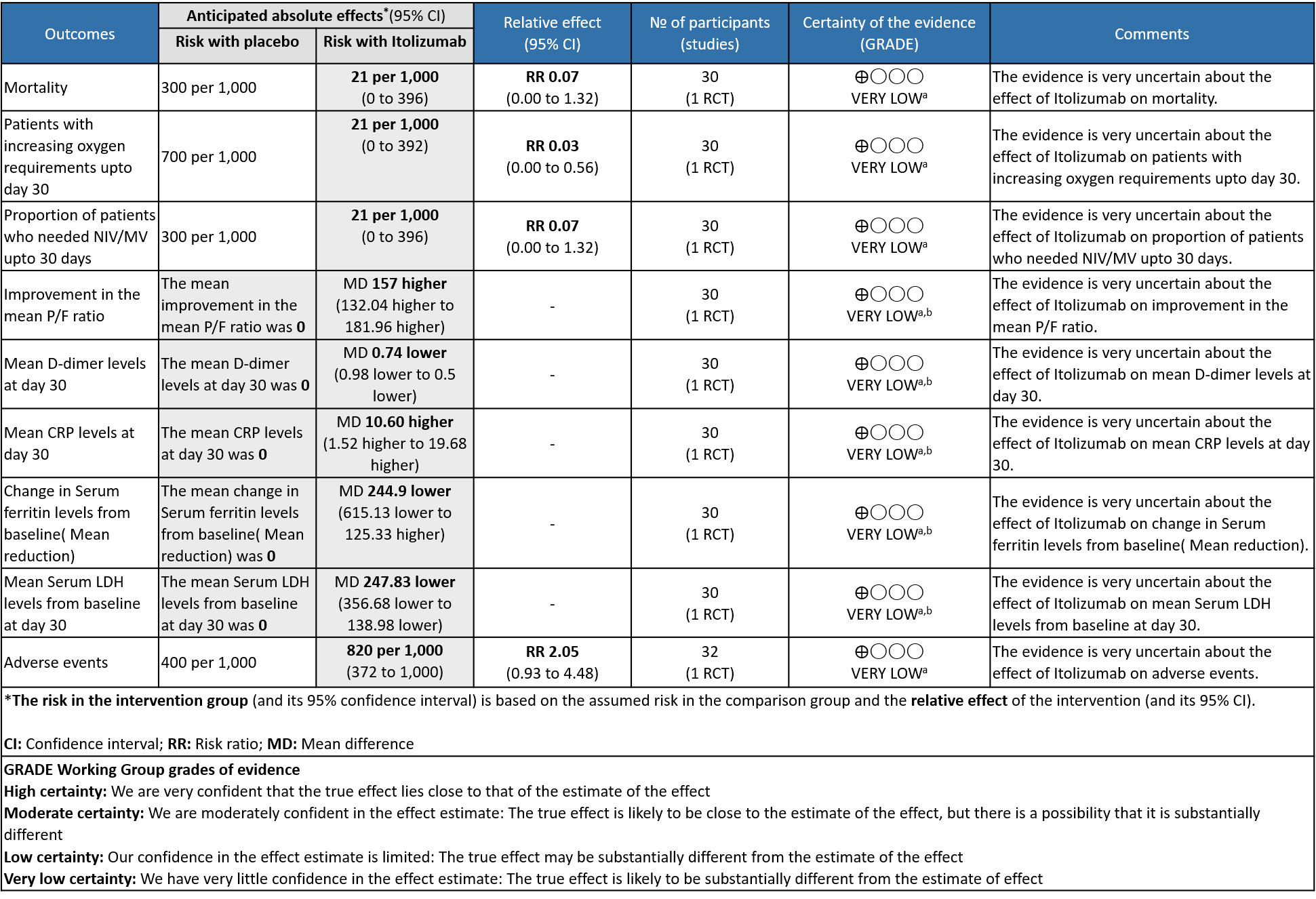
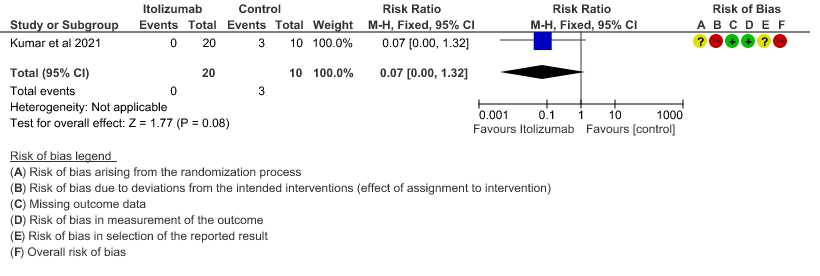
- All-cause mortality at 28 days: Very low certainty of evidence in 30 patients from 1 RCT2 including those with moderate to severe COVID-19 infection, showed that Itolizumab had a very uncertain effect on the mortality at day 28 RR 0.07 (95% CI 0.00 to 1.32).
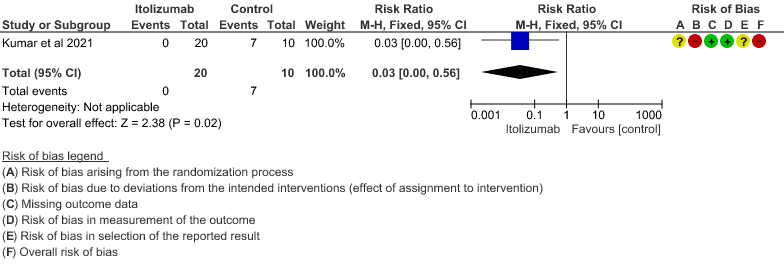
- Patients with increasing oxygen requirements upto day 30: Very low certainty of evidence in 30 patients from 1 RCT2revealed a very uncertain effect of Itolizumab on increasing oxygen requirements RR 0.03
(95% CI 0.00 to 0.56). This suggested a very imprecise estimate that Itolizumab reduced the proportion of those needing increased oxygen requirements upto day 30 by 97% but this could vary from 44% to 100%. - Need for non- invasive/mechanical ventilation: Very low certainty of evidence in 30 patients from 1 RCT2revealed a very uncertain effect of Itolizumab on the need for NIV/mechanical ventilation upto 30 days RR 0.07(0.00 to 1.32). This suggested a very imprecise estimate of Itolizumab reducing the need for NIV/Mechanical ventilation by 93%( 95% CI 100% reduction or 32% increase).
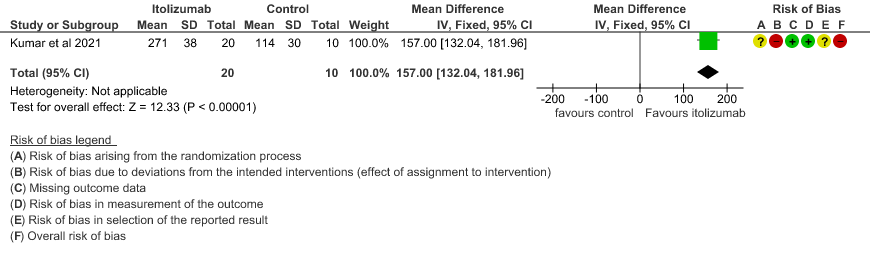
- Improvement in the PF ratio: Very low certainty of evidence in 30 patients from 1 RCT2revealed a very uncertain effect of Itolizumab on improvement in PF ratio with mean difference MD 157 higher(95% CI 132.04 to 181.96 higher) as compared to placebo.
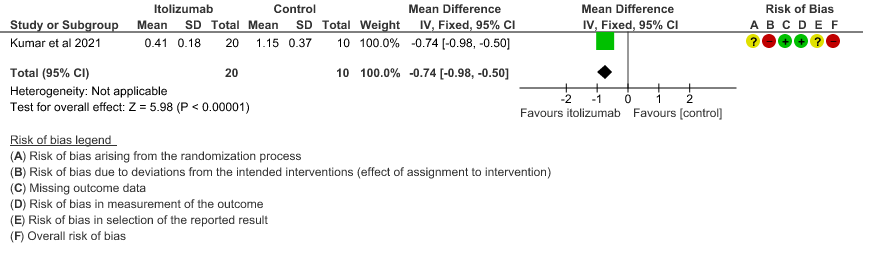
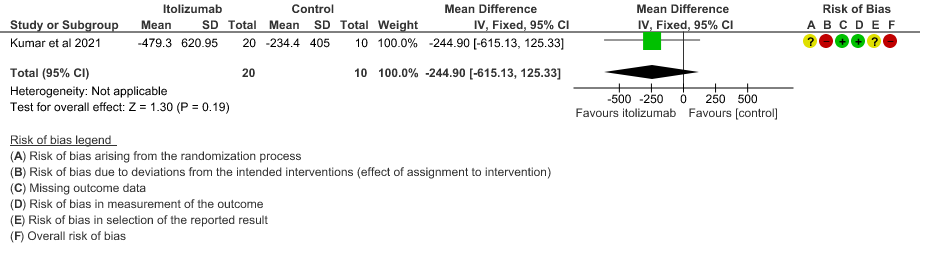
- Mean D-dimer levels at day 30: Very low certainty of evidence in 30 patients from 1 RCT2revealed a very uncertain effect of Itolizumab on mean D-dimer levels at day 30; MD was 0.74 lower (95% CI 0.5 - 0.98 lower). Baseline D-dimer level was higher in the control to begin with 5.15 (SD 7.85) μg/mL compared to Itolizumab arm 3.50 (SD 4.87) μg/mL. The mean D-dimer reduced to 2.83 (SD 5.46) μg/mL and 0.41 (SD 0.18) μg/mL on Days 14 and 30, respectively in the Itolizumab group. In control group, mean D-dimer was 0.86 (SD 0.71) μg/mL and 1.15 (SD 0.37) μg/mL on Days 14 and 30, respectively.
- Mean CRP levels at day 30: Very low certainty of evidence in 30 patients from 1 RCT2revealed a very uncertain effect of Itolizumab on the baseline CRP levels. Baseline C-reactive protein (CRP) was numerically higher in control group 103.88 (SD 87.89) mg/L vs 73.74 (SD 71.84) mg/L in the intervention group. In the Itolizumab group, mean CRP reduced to 6.45 (SD 4.14) mg/L and 13.69 (SD 20.45) mg/L on Days 14 and 30, respectively. In the control group, mean CRP reduced to 14.36 (9.29) mg/ L and 3.05 (2.62) mg/L on Days 14 and 30, respectively.
- Mean reduction in serum Ferritin levels from baseline: Very low certainty of evidence in 30 patients from 1 RCT2revealed a very uncertain effect of Itolizumab on reduction in Serum ferritin levels from baseline(Mean reduction) MD 244.9 lower(95% CI 615.13 lower to 125.33 higher). Baseline ferritin was high in Itolizumab group compared to control (943.34 ng/mL vs 577.95 ng/mL). In Itolizumab arm the mean ferritin reduced to 303.50 (SD 210.93) ng/dL and 189.22 (SD 129.96) ng/dL on Day 14 and 30, respectively. In control group, ferritin was 367.68 (SD 130.22) ng/dL and 285.25 (SD 157.76) ng/dL on Days 14 and 30, respectively. This suggested that a greater reduction from baseline was seen in serum ferritin levels in Itolizumab arm (−479.3 (620.95) ng/dL) in comparison to control (−234.4 (405.67) ng/dL) at day 30 (p-value = 0.078).
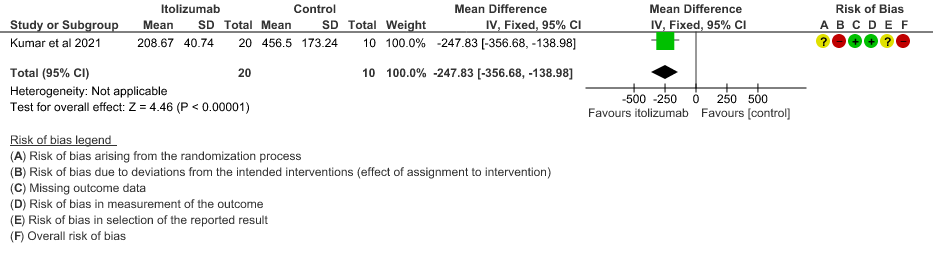
- Mean Serum LDH levels from baseline at day 30: Very low certainty of evidence in 30 patients from 1 RCT2revealed a very uncertain effect of Itolizumab on mean Serum LDH levels from baseline on day 30 ;MD 247.83 lower(95% CI 356.68 lower to 138.98 lower). Baseline lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was comparable in both arms; 533.30 (SD 206.85) U/L in Arm-A and 645.30 (SD 292.79) U/L in Arm-B. In the Itolizumab arm, mean LDH reduced to 381.47 (SD 181.45) U/L and 208.67 (SD 40.72) U/L on Days 14 and 30, respectively. In the control arm, mean LDH was 330.20 (SD 91.63) U/L and 456.50 (SD 173.24) U/L on Days 14 and 30, respectively.
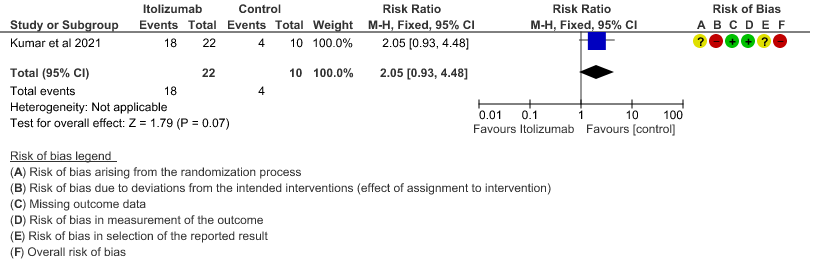
- All adverse events:Very low certainty of evidence in 30 patients from 1 RCT2revealed a very uncertain effect of Itolizumab on all adverse events. Based on the data, we anticipate that for 1000 patients with COVID-19 disease treated with placebo 400 adverse events are likely. We anticipate that there would be 420 higher (320 to 1000) adverse events per 1000 people if Itolizumab is administered for patients with COVID-19. This was due to the fact that 18 adverse events related to the drug occurred in the patients treated with Itolizumab(N=22) among those 30 patients studied in our trial. Two patients had infusion reactions with Itolizumab infusion and hence the drug was not given. Considering that was a single trial conducted among 30 patients, of which 20 patients received Itolizumab with high risk of bias in RoB2 tool, the evidence is very uncertain about the effect of Itolizumab on adverse events.
ITOLIZUMAB COMPARED TO SOC IN PATIENTS WITH MODERATE TO SEVERE COVID 19.
1. Mortality at day 28

2. Patients with increasing oxygen requirements at day 30
3. Need for NIV/Mechanical ventilation at day 30
4. Improvement in the PF ratio
5. Mean D-dimer levels at day 30
6. Mean CRP levels at day 30
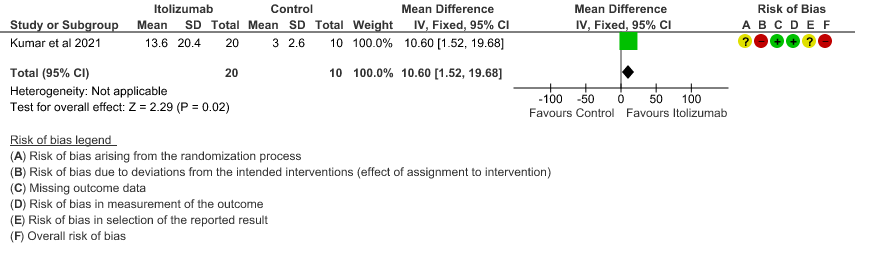
7. Mean reduction in serum Ferritin levels from baseline
8. Mean Serum LDH levels from baseline at day 30
9. All adverse events